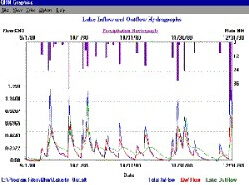
QHM - 水流模拟软件
QHM 软件是基于Windows系统的水域连续流量和质量模拟模型,主要用于水域管理和雨水设计。
该项目也可以作为的教学工具。大多数应用是流域分析,通常与雨水较好的管理措施的选择和规模有关,是流量控制和处理池。QHM为流域管理者和雨水控制系统的设计者提供了规划和设计工具。
QHM能够连续模拟:
-
地表径流和底流
-
储层路由
-
土壤冻融
-
融雪和除雪/处置
-
蒸发和土壤水分蒸发蒸腾损失总量
-
污染物的产生和排放
-
流侵蚀潜在QHM模拟可以表示不确定长度的周期(可用磁盘空间限制)。该模型可用于离散事件或多事件连续的基础上。
QHM成分
可以模拟的成分有:雨水径流(流量和体积),可选的有一种多多种组合:一种污染物表现出一阶衰减或使用额定曲线模拟的;以离散颗粒沉降为的沉积物(5个粒度类别);以及累积过量边界剪切应力的河流侵蚀指数。
在地方获得的流量和污染物记录(检测或模拟模型)可以通过该模型在池塘或河流河段进行路由。
QHM系统组件,可以模拟的系统组件有:
-
集雨
-
滞留池
-
水库
-
可能有汇合点和分岔(水流分叉)的河段
-
由上述任意组合和任意数量的组件组成的系统可以被模拟,条件是系统的组件和系统作为整体可以被描述为“单向的”或“无反馈的”。
-
循环网络,或流出取决于接收通道水深的池塘,是在这个模型中能很好的表示情况的例子,适用于QHM的典型应用是树枝状河网,其河道均匀流动条件充分表示。
QHM组织
当QHM程序打开时,用户可以从七个选项中进行选择,其中四个选项代表标准的Windows实用程序。三个是于QHM的:帮助、运行和实用程序;这些将在这里介绍,并在下面进行更详细的解释。
除了Windows帮助之外,帮助菜单还用户手册的内容。
运行菜单三个命令:
-
运行QHM启动模拟运行使用在实用工具/设置运行选项下提供的信息;如果由用户指定,将在运行开始之前显示这些选项。
-
输入接口,如下所述,允许用户创建新的输入文件。有些用户更喜欢使用文件和编辑命令创建文件来修改现有文件。
-
PLOT GRAPH用于选择,查看和打印之前使用UTILITY / CREATE GRAPH命令创建的图形。
工具还三个命令:
-
将降水、温度和流量的标准格式转换为标准格式。它还可以用来忽略模拟运行要的气象数据,并从文件中三处QHG无法识别的错误代码。
创建图形温江标识要通过RUN / PLOT、GRAPH命令查看和打印的图形的文件和模拟周期。 -
设置运行选项允许确定文件将在下一次模拟运行中使用;在模拟运行期间,是否显示当前正在执行的命令的名称;以及模拟运行完成时显示的输出(如果选择前选项,则不可用此选项)。
-
默认按钮将显示用户喜欢的设置。
【英文介绍】
QHM is a Windows-based continuous watershed quantity and quality simulation model intended for watershed management and stormwater design. The program can also be used as an effective teaching tool. Most applications have been watershed analysis usually related to selection and sizing of stormwater BMPs, particularly, flow control and treatment ponds. QHM offers an important planning and design tool to watershed managers and designers of stormwater quantity and quality control systems.
QHM is capable of continuous simulation of:
Surface runoff and base flow
Detention pond routing
Reservoir routing
Soil freeze-thaw
Snowmelt and snow removal/disposal
Evaporation and evapotranspiration
Pollutant generation and routing
Stream erosion potential
QHM is capable of continuous simulation of:
Surface runoff and base flow
Detention pond routing
Reservoir routing
Soil freeze-thaw
Snowmelt and snow removal/disposal
Evaporation and evapotranspiration
Pollutant generation and routing
Stream erosion potential
QHM simulation can represent a period of indefinite length (limited only by available disk space). The model can be used on a discrete event or multi-event continuous basis.
QHM Constituents
Constituents that can be simulated are: stormwater runoff (flow rate and volume) and, optionally, one or any combination of: one pollutant exhibiting first-order decay or characteristics simulated using a rating curve; sediments (in up to five size fractions) characterized by discrete particle settling; and instream erosion indices based on cumulative excess boundary shear stress.
Appropriate flow and pollutant records obtained elsewhere (monitoring or other simulation models) can be routed through ponds or river reaches by the model.
QHM System Components
Components of a physical system that can be simulated are:
Catchments
Detention ponds
Reservoirs
River reaches which may have junctions and bifurcation (flow splits)
A system comprised of any combination and any number of the above components can be simulated provided that each component of the system and the system as a whole can be described as "one-way" or "non-feedback."
Looping networks, or ponds where outflow depends on water depth in the receiving channel, are examples of situations which might not be well-represented in this model. A typical application appropriate for QHM would be a dendritic river network with channels adequately represented by uniform flow conditions.
QHM ORGANIZATION
When the QHM program opens, the user can select from seven options of which four represent standard Windows utilities. The other three are specific to QHM: HELP, RUN, and UTILITY; these are introduced here and explained in more detail below.
The HELP menu includes, in addition to Windows Help, the complete contents of the user's manual.

The RUN menu includes three commands:
RUN QHM starts a simulation run using information provided under UTILITY/SET RUN OPTIONS; if specified by the user, the options will be displayed before the run commences.
INPUT INTERFACE, which is described below, allows the user to create a new input file. Some users will prefer to create a new file using the FILE and EDIT commands to modify an existing file.
PLOT GRAPH is used to select, view, and print a graph previously created using the UTILITY/CREATE GRAPH command.
UTILITY also includes three commands:
CONVERT DATA FORMAT changes standard data formats for precipitation, temperature, and flow into other standard formats. It can also be used to ignore meteorological data that is not needed for a simulation run, and to remove from a file, error codes that will not be recognized by QHM.
CREATE GRAPH FILE will identify files and simulation periods for a graph to be viewed and printed by the RUN/PLOT, GRAPH command.
SET RUN OPTIONS allows determination of the files to be used in the next simulation run; whether, during a simulation run, the name of the command that is currently being executed will be displayed; and the output to be displayed when a simulation run is complete (this option is not available if the previous one is selected).
The DEFAULT button will display settings that many users prefer.

The QHM program is structured as a series of commands which are summarized in the PROGRAMS COMMAND section herein and described in detail in the user's manual.
GETTING STARTED WITH QHM
This section summarizes information that a user must have at hand before using QHM. Appendix A of the user's manual includes three step-by-step exercises that will guide a first-time user through the basic operation of QHM.
Defining the Problem
It is assumed that the user has identified the problem that the simulation will address:
What is to be simulated - flow; quality parameters; stream erosion; snow removal
Calibration - flow; quality
System components and configuration - a system schematic; identifying sub-watersheds; stream reaches; ponds; and reservoirs
QHM Input Data

Further details about input data requirements and file formats are provided in the INPUT DATA section of the user's manual. Required data includes:
Meteorological data as required by the proposed simulation - precipitation file, extension .pre; temperature file, extension .tmp; evaporation data, to be entered in input file
Calibration data - flow, extension .flo; quality, extension depends on parameter
Input file formats must be standard formats that are recognized by QHM and must be identified during program setup.
QHM Output
In the input file, the user will specify the nature and form of outputs required after a simulation run: each output file is identified in terms of a Series and ID number. The program, in UTILITY/SET RUN OPTIONS, will ask the user to select the name and extension for the output file and to select output options.
QHM ID and Series Numbers
An ID number is used by QHM to identify a file that contains a time series of flow data that is generated by the program. ID numbers are assigned by the user to identify a flow series at the outlet of a sub-watershed, watershed, pond, reservoir, or channel. Because output quality data, if generated, will be contained in the same file as the flow data, they will also be identified by the same ID number.
The maximum number of flow series files that is retained by the program is 24. If a simulation run creates more than 24 flow series, the user must decide which of the previously created files will be overwritten in order to reassign the ID number to another series; the data in the overwritten files will be lost. In many cases this will not matter, e.g., after flows simulated for two sub-watersheds are combined, the individual files may not be of interest.
If the user wants to retain a record of a flow series before an ID number is reassigned, that series can be recorded by the PRINT SERIES, DUMP PRINT, or DUMP PLOT commands.
In addition to an ID number, each outflow series is also assigned a Series Number. Series Numbers are not recognized by the program; they are intended to allow the user to keep track of files when many files are generated by a single simulation run.
If a simulation run does not generate more than 24 flow series, they will all be identified by their ID numbers; in this case Series Numbers, although they must be entered, will be redundant, and dummy values can be used.
QHM Time Steps
Input data time steps may be 5, 10, 15, 20, 30 or 60 minutes, or 24 hours, for precipitation; monthly for evaporation; or hourly or daily for flow.
The program can be instructed to perform calculations based on any specified time step. If the calculation time step is less than the precipitation time step, the program will use the average precipitation value in each calculation time step. If the calculation time step exceeds the precipitation time step, the latter will be used as the calculation time step.
Time steps for input precipitation data are specified in the START command. Calculation time steps are specified in the GENERATE command. If a flow series not generated by the program is to be provided using the STORE command, the data input time step will be identified under that command. The routing time step for the POND, RESERVOIR, and REACH commands is specified in those commands.
QHM SAMPLE FILES
Table 1 lists sample input files that are included with the program, sample data files that are recognized by each input file and indicates the program command that the input file is intended to illustrate. It also indicates the data format of each sample data file.
TABLE 1 - QHM SAMPLE INPUT FILES
File Name
TEST_GEN.INP
TEST_EVAP.INP
TEST_BSFLW.INP
TEST_RES.INP
TEST_SPL.INP
TEST_QUA.INP
TEST_RCH.INP
TEST_SNO.INP
TEST_SRM.INP
TEST_ERSN.INP
TEST_POND.INP
TEST_BAT.INP
TEST_EVENT.INP
Associated Files
RAIN85.PRE
RAIN85.PRE
RAIN85.PRE
2YR.PRE
CAL65.PRE
RAIN85.PRE
2YR.PRE
SNOW.PRE
SNOW.TMP+SNOW.PRE
2YR.PRE
RAIN90.PRE
2YR.PRE
EVENT10.PRE
Purpose is to test:
GENERATE COMMAND
EVAPORATION IN GENERATE
COMMAND
BASE FLOW ALGORITHM
ROUTE RESERVOIR COMMAND
SPLIT SERIES COMMAND
POLLUTION GENERATION
REACH COMMAND FOR STREAM ROUTING
WINTER SEASON SIMULATION
SNOW REMOVAL/DISPOSAL
INSTREAM EROSION INDEXES
POND COMMAND
BATCH POND OPERATION
FREE FORMAT RAINFALL OPTION
TABLE 2 - QHM SAMPLE DATA FILES
File Name
2 YR.PRE
CAL_65.PRE
RAIN85.PRE
RAIN90.PRE
SNOW.PRE
SNOW.TMP
FLOW.FLO
HEC.FLO
EVENT_10.PRE
EVENT_15.PRE
EVENT_30.PRE
EVENT_5.PRE
Description
rainfall data
rainfall data
rainfall data
rainfall data
winter precipitation data
temperature data file
flow sample file
flow sample file
rainfall data
rainfall data
rainfall data
rainfall data
Data Period
81-06-10 - 81-06-30
65-05-01 - 66-04-01
85-02-01 - 85-12-31
90-06-01 - 90-10-29
70-11-02 - 71-05-04
83-01-03 - 87-04-10
70-11-01 - 71-05-04
92-05-30 - 92-06-30
92-05-30 - 92-06-30
97-08-07 - 97-08-09
97-08-07 - 97-08-09
97-08-07 - 97-08-09
97-08-07 - 97-08-09
Data Format
AES Hourly
AES Hourly
HEC Hourly
HEC Hourly
AES Hourly
AES Hourly
AES Hourly
IWD Hourly
HEC Hourly
10min. file
15min. file
30min. file
5min. file
- 2025-05-07
- 2025-04-29
- 2025-04-21
- 2025-04-18
- 2025-04-11
- 2025-04-10
- 2025-05-07
- 2025-04-17
- 2025-04-15
- 2025-04-14
- 2025-04-11
- 2025-04-01